Japp–Klingemann Reaction on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Japp–Klingemann reaction is a  The hydrazone products of the Japp–Klingemann reaction are most often used as intermediates in syntheses of more complex organic molecules. For example, a phenylhydrazone product can be heated in the presence of strong acid to produce an
The hydrazone products of the Japp–Klingemann reaction are most often used as intermediates in syntheses of more complex organic molecules. For example, a phenylhydrazone product can be heated in the presence of strong acid to produce an 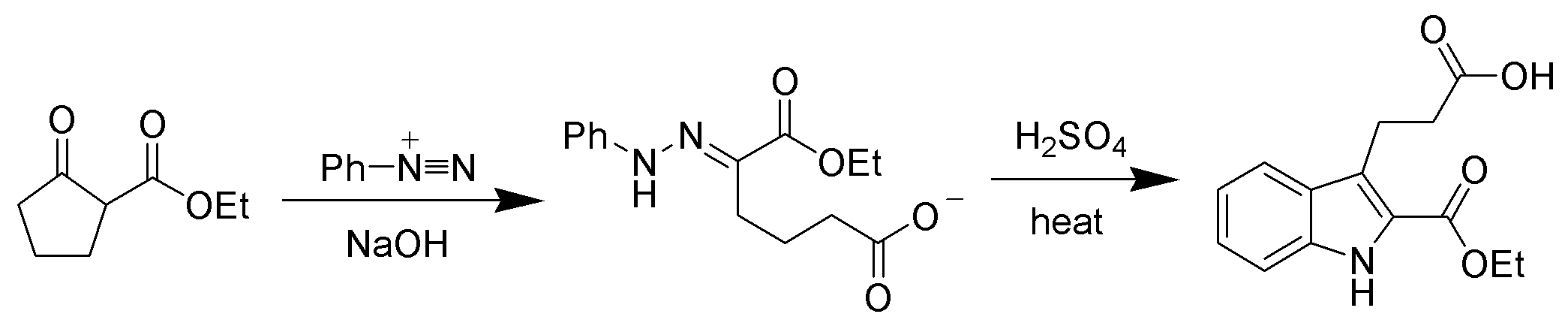 If there is a
If there is a 

chemical reaction
A chemical reaction is a process that leads to the IUPAC nomenclature for organic transformations, chemical transformation of one set of chemical substances to another. Classically, chemical reactions encompass changes that only involve the pos ...
used to synthesize hydrazone
Hydrazones are a class of organic compounds with the structure . They are related to ketones and aldehydes by the replacement of the oxygen =O with the = functional group. They are formed usually by the action of hydrazine on ketones or aldehydes. ...
s from β-keto-acids (or β-keto-esters) and aryl
In organic chemistry, an aryl is any functional group or substituent derived from an aromatic ring, usually an aromatic hydrocarbon, such as phenyl and naphthyl. "Aryl" is used for the sake of abbreviation or generalization, and "Ar" is used as ...
diazonium salt
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.
General properti ...
s. The reaction is named after the chemists Francis Robert Japp
Francis Robert Japp FRS (8 February 1848 – 1 August 1925) was a British chemist who discovered the Japp-Klingemann reaction in 1887.
He was born in Dundee, Scotland, the son of James Japp, a minister of the Catholic Apostolic Church. He grad ...
and Felix Klingemann.
: The hydrazone products of the Japp–Klingemann reaction are most often used as intermediates in syntheses of more complex organic molecules. For example, a phenylhydrazone product can be heated in the presence of strong acid to produce an
The hydrazone products of the Japp–Klingemann reaction are most often used as intermediates in syntheses of more complex organic molecules. For example, a phenylhydrazone product can be heated in the presence of strong acid to produce an indole
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C8 H7 N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indole is widely distributed in the natural environmen ...
via the Fischer indole synthesis
The Fischer indole synthesis is a chemical reaction that produces the aromatic heterocycle indole from a (substituted) phenylhydrazine and an aldehyde or ketone under acidic conditions. The reaction was discovered in 1883 by Emil Fischer. Today ...
.
: If there is a
If there is a leaving group In chemistry, a leaving group is defined by the IUPAC as an atom or group of atoms that detaches from the main or residual part of a substrate during a reaction or elementary step of a reaction. However, in common usage, the term is often limited t ...
elsewhere in the Japp–Klingemann product, the hydrazone instead can cyclize at that site via a substitution reaction
A substitution reaction (also known as single displacement reaction or single substitution reaction) is a chemical reaction during which one functional group in a chemical compound is replaced by another functional group. Substitution reactions ar ...
to give a pyrazole
Pyrazole is an organic compound with the formula C3H3N2H. It is a heterocycle characterized by a 5-membered ring of three carbon atoms and two adjacent nitrogen atoms, which are in ortho-substitution. Pyrazole is a weak base, with p''K''b 11.5 ( ...
. This process is a key part of the synthesis of and related compounds:

Reaction mechanism
To illustrate the mechanism, the Japp-Klingemann ester variation will be considered. The first step is thedeprotonation
Deprotonation (or dehydronation) is the removal (transfer) of a proton (or hydron, or hydrogen cation), (H+) from a Brønsted–Lowry acid in an acid–base reaction.Henry Jakubowski, Biochemistry Online Chapter 2A3, https://employees.csbsju.ed ...
of the β-keto-ester. The nucleophilic addition
In organic chemistry, a nucleophilic addition reaction is an addition reaction where a chemical compound with an electrophilic double or triple bond reacts with a nucleophile, such that the double or triple bond is broken. Nucleophilic additions di ...
of the enolate
In organic chemistry, enolates are organic anions derived from the deprotonation of carbonyl () compounds. Rarely isolated, they are widely used as reagents in the synthesis of organic compounds.
Bonding and structure
Enolate anions are electr ...
anion 2 to the diazonium salt
Diazonium compounds or diazonium salts are a group of organic compounds sharing a common functional group where R can be any organic group, such as an alkyl or an aryl, and X is an inorganic or organic anion, such as a halide.
General properti ...
produces the azo compound
Azo compounds are organic compounds bearing the functional group diazenyl (, in which R and R′ can be either aryl or alkyl groups).
IUPAC defines azo compounds as: "Derivatives of diazene (diimide), , wherein both hydrogens are substituted ...
3. Intermediate 3 has been isolated in rare cases. However, in most cases, the hydrolysis of intermediate 3 produces a tetrahedral
In geometry, a tetrahedron (plural: tetrahedra or tetrahedrons), also known as a triangular pyramid, is a polyhedron composed of four triangular faces, six straight edges, and four vertex corners. The tetrahedron is the simplest of all the o ...
intermediate 4, which quickly decomposes to release the carboxylic acid 6. After hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, an ...
exchange, the final hydrazone 7 is produced.

References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Japp-Klingemann reaction Substitution reactions Name reactions